- Introduction to web
- The Structure of a HTML document
- HTML Tags & Forms
- CSS
Lecture 2: HTML, CSS - Structure & Content
Web Programming
J Mwaura
Lecture Outline
Website
Website - collection of related web pages that are normally stored on a single web server computer
Web server - computer system that enables users to access web pages stored on the web server's computer
To create a website, need the following;
- A text editor
- An upload/publishing tool
- A web hosting service
- A browser
Web map - a map that is powered by the web. Its internet dependent, interactive and not always self-contained
Web map
Powered by
- Web technology
- Server-side communication
- Draws data from outside sources
- Real-time, live data feeds

Structure of a HTML document
HTML uses some predefined tags to display a particular given content
Types of tags
- Singular tags - no closing tags
<...> - Paired tags - have both opening
<...>and closing</...>tags
Structure of a HTML document
A HTML document has 2 sections;
- Head - contains the information about the HTML document. e.g., metadata, title, page CSS etc
- Body - contains everything you want to display

HTML Tags & Forms
Document structure tags
- HTML tag - specify that the document is html
- Head tag - contain all the head element e.g. title, style, meta, etc
- Boby tag - defines the body of html document e.g. image, tables, lists, etc
- Form tag - used to create html form for user
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
CSS - Making your document look good, by adding formatting to your web pages
In style tag, includes a type attribute with a value of "text/css"
The formatting rules/statements go inside a style container
Each rule/statement has a CSS property and a CSS value, separated by full colon
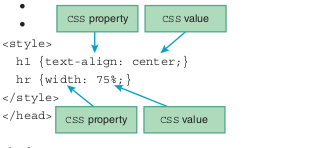
CSS Style

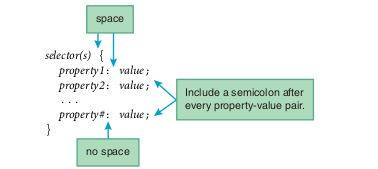
CSS Rules
CSS rules are applied to elements using selectors
- Type selectors - (e.g.,
hr {width: 50%;}) to match & format all instances of the element type - Universal selectors - uses
*or asterisk - wildcard (e.g.,* {text-align: center;}). all that matches every item in a collection of things are formatted - Class Selectors

Class Selectors
The dot thing is called a class selector - select elements that have a particular value for their class attribute
.red, .conspicuous, h1 {background-color: tomato;}
Class selector with an element type prefix
q.blue {background-color: skyblue;}
q.blue matches elements that have a class attribute value of "blue". But it's a more specific selector that it looks for class="blue" only in q elements
Class selector with * prefix e.g. *.big-warning {font-size: x-large;}
ID Selectors
An ID selector uses an element's id attribute
A significant feature of an id attribute is that its value must be unique within a particular web page

span & div Elements
span is a phrasing element
div is a block element
The div & span elements surround text that doesn't fit very well with other elements
CSS Properties

Examples
End of Lecture 2
Web Programming
That's it!
Queries about this Lesson, please send them to:
*References*
- Google Maps; Power Tools for Maximizing the API, 2014
Evangelos Petroutsos- D3 Tips and Tricks; Interactive Data Visualization in a Web Browser, 2013
Malcolm Maclean- Interactive Data Visualization for the Web, 2013
Scott Murray- Web Programming with HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript, 2019
John Dean- Leaflet Documentation
Leaflet Team- Google Documentation for developers
Google Team
Courtesy of …