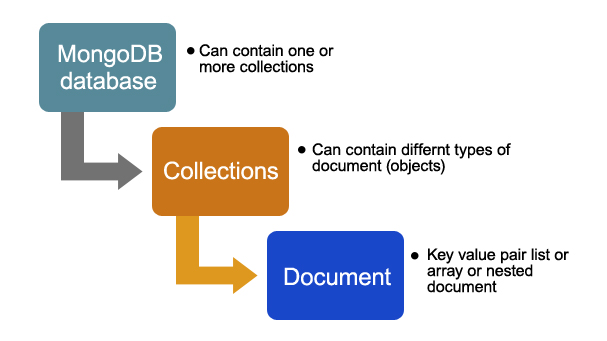
Supports scaling and geospatial indexing capabilities
No concepts of tables, rows, columns
No features of ACID compliance, JOINS, foreign keys etc
MongoDB stores data as Binary JSON Documents (also known as BSON)
MongoDB is built for scalability, performance and high-availability