- Lectures
- Online tutorials
- Problem-based Learning(s)
- Assignment(s)
- Presentation(s)
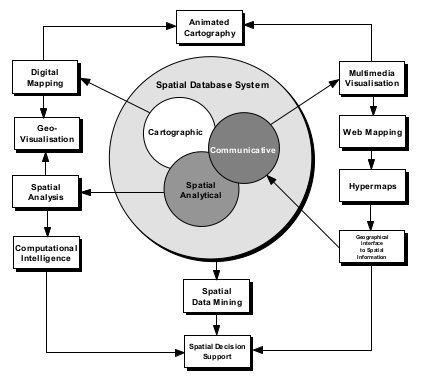
There are 4 functional aspects of spatial information, namely;
Spatial database system are powered by its spatial indexing and data processing capabilities for various applications
A new conceptualisation for spatial information functions
Others
In today's world, data is all over(abundant, global, everywhere) & pervasive(unescapable, prevalent, persistent)
Databases, are specialized structures that allow computer-based systems to store, manage, and retrieve data very quickly
From birth to death, we generate and consume data.
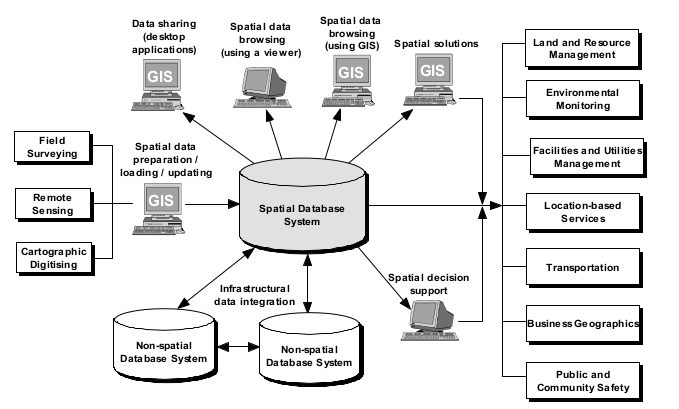
A typical spatial database system is an ordinary database with additional capabilities and functions to handle spatial data
These capabilities and functions are
SDS represent a data-based and user-centric approach to spatial information in 3 dimensions, namely;
Stewardship - custodian of information mandated by lawSharing - spread the cost across units with organizationCommodification - ownership in data and information, sales of value
Single-user
Workgroup
Enterprise database
Consortium database
Typical strategy for migrating from GIS to SDS

Robust core of GIS being DBMS is certainly a trend that continues
Technologies mature and grow together
Project management principles and skills are increasingly important
Decision support applications of spatial databases are becoming increasingly important
User Needs Assessment (UNA) is a term similar to:
Systems analysis - understand workings of system by decomposing the work activityFunctional requirements study - what capabilities are neededBusiness functions - what business functions are to be supportedRequirements engineering - specification of functional capabilities neededUser need defines what a typical user requires of a database
But the challenges vary according to
Facilitate knowledge transfer and integration between users and designers
Identify business problems and associated business function activities
Provide coherent framework for business information objects and activities
Evaluate the functional feasibility of proposed database
Structured and systematic approach for identifying desired system functions
Reconcile different user needs associated with business functions and activities
Outline framework for sharable information services and interoperability
Document analysis - scour documents for insights about what is to be done
Job observations - participant observation of information work activity
Questionnaires - ask questions about activities
Interviews - face-to-face discussion about information activity
Focus group discussion - brainstorming sessions get people to share insights
Needs development
Needs management
Documentation of the outcomes
Development
Management
Queries about this Lesson, please send them to:
*References*
- Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Project Management, Springer.
Albert K W Yeung & G. Brent Hall- Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management, 12th ed.
Carlos Coronel & Steven Morris- Database Modeling and Design; Logical Design, 5th ed.
Taby Teorey et.al- Fundamentals of database systems, 6th ed.
Ramez Elmasri & Shamkant B. Navathe
Courtesy of …